Scarcity
Scarcity refers to the unavailability of a certain commodity in the market. The conceptual meaning of scarcity, in economics is different. A commodity is a scare, in an economic sense not because it is rare or unavailable in the market, but because the means to have are limited. We have limited resources at our disposal, so there is a problem of scarcity. Human wants are unlimited but the resources to satisfy the human are limited.
We need goods and services to satisfy our wants. For this purpose, we need resources that may be classified as land, labor and capital which are limited in relation to their demand. For example, land can be used to raise agricultural crops, to construct factory, buildings, to layout parks, etc. Our wants are unlimited and the resources to satisfy them are limited. Scarcity explains the relation between the limited resources and unlimited want and need of the human beings and problem therein.
Thus, scarcity is at the heart of all economic problems. It reflects the imbalance between society’s demand for resources and their supplies. Since human wants are unlimited and the resources available are limited, scarcity is perpetual and universal.
Choice
The choice is involved in economic activities at both consumption and production levels. It also concerns individual and the state. The problem of choice begins with an individual, liking of how much time he would allot for work and how much for leisure. At the same time the more he work, the more he earns. On the income earned, the choice is between how much to consume and how much to save. Choice in consumption means what to buy.
Since the resources are scarce, society must decide which want will be satisfied and which want will not. Maximum satisfaction should be obtained by utilizing the productive resources that are available in a useful manner. Our choice has to be such that the most of our want be satisfied because the demand for the resources is more than their availability.
The stock of land in Nepal is limited. But land has alternative uses. If more wheat is to produce, the land has to be diverted from other uses (e.g. production of vegetables).
Allocation of Resources
Allocation of resources is defined as the process of selection of resources and their proper utilization. Various types of resources are required to produce goods and services.
The main problem relating to the proper allocation of the resources are explained as follows:
What to produce
The first concern is related with what to produce? The problems such as what to produce are to be produced and in what quantities arise directly from the scarcity of resources. Production must meet the maximum social need as it is the first priority. The social norms and values should guide to maximize social satisfaction. The problem of what to produce and how much to produce depends on the necessity of the citizens of the country.
How to produce
The second concern is related to the method of production. In some cases, labour may play a major role. It is called labour-intensive technology. It is called capital-intensive. Labour intensive method creates more jobs favouring more employment. Capital-intensive production goes for a large volume of production. The right decision depends on the current state of the economy.
For whom to produce
It can be expressed as how to distribute society is total product among its different units? Or, how the total national product distributed among the different factors of production or among the different individuals and families? The distribution of the output of society among its various members must be determined.
Balance in Development
While allocating the resource, a nation must give the priority to maintain the sector balance in development. The balance between rural and urban, consumer goods and exported goods, balance in the sector of development (primary, secondary, tertiary sector).
Production Possibility Curve
Production is the creation of utility. It transfers raw materials into goods and services. Due to the scarcity of resources, we cannot produce the unlimited want of production. If all the resources are used to produce only one commodity then there will be no more resources for the next commodity. In order to manufacture the goods, the resources must be allocated.
Production possibility curve (PPC) represents the maximum amount of a pair of goods or service that can both produce with an economy is given resources and technique, assuming that all resources are fully employed. The PPC is the graphical presentation of alternative production possibilities in an economy. It is also called as production possibility boundary or frontier because it shows the limit of what it is possible to produce with the available limited resources. Some of the assumptions of PPC are given below:-
- An economy is producing only two goods.
- There is full employment.
- The technology used in the production is constant.
- Factors of production are given and fix.
- The time period is given and fix.
The PPC can be explained with the help of the following table:
| Combinations | Goods “X” | Goods “Y” |
| A | 0 | 15 |
| B | 1 | 14 |
| C | 2 | 12 |
| D | 3 | 9 |
| E | 4 | 5 |
| F | 5 | 0 |
The above table illustrates the production of any two commodities as good ‘x’ and good ‘y’. When all the resources are used to produce goods ‘y’ only a producer can produce 15 units of goods without the production of good ‘x’. If the production is obtained from ‘F’ then 5 units of ‘x’ good will be produced without the production of ‘y’ goods. Besides these, there are many possibilities of production such as B, C, D and E and A to B, B to C and so on shows that the production of goods ‘x’ steps up. This PPC can be shown in the following graph.

In the figure good ‘x’ are represented on the x-axis and good ‘y’ on the y-axis. AF is the production possibility curve (PPC) which is made by joining various points. A, B, C, D, E and F. It slopes concave to the origin because of the operation law of increasing marginal rate of technical substitution. The sacrificing rate of good ‘y’ goes on increasing as the production of good ‘x’ increases.
Shifting in PPC
The PPC shifts left-hand side and right-hand side. The right hand side shift PPC indicates an increase in production and left-hand side decrease in the production.Some of the reasons for shifting PPC are as below:
Change in resources
When the supply of raw material increases the production also increases so the PPC shift upward. And if decreases than PPC shift downward.
Change in the efficiency of labour
When the efficiency of labour increases by any means the production can be increased with the PPC shift upward. And if decreases then PPC shifts downward.
Change in Technology
When the advance technology is used instead of traditional technology in the production prices the production capacity increase & PPC shift upward. And if the traditional technology is used instead of advanced technology then the PPC curve shift downward.
Change in Investment
When the investment increase in the production the production also increases so, the PPC shifts upward. And when investment decreases PPC curve slopes downward.
Exercise
Very Short Questions ( For 1 Marks )
- Define scarcity with example.
Answer: Scarcity is the situation in which our wants and needs exceed the available resources. For example: Land, Building, Machines etc. are scarce as their supply in the economy is less than the demands. - State the meaning of choice.
Answer: Choice is the act of fulfilling one want out of many wants in which the rational consumer calculates and compares the different alternatives and chooses the alternative highest in the ranking. The consumer does so to maximize his/her satisfaction. - State the meaning of opportunity cost with example.
Answer: The second best alternative that has been sacrificed by an economic agent while taking any best decision is called opportunity cost. It is also the best alternative that has been forgone. For example: Suppose a farmer has fixed resources i.e. one ropanee of land. At a season, either he can produce either 30 kg of rice or 20 kg of maize. If the farmer decides to produce rice, its opportunity cost is 20 kg of maize which has been forgone. - Define allocation of resources.
Answer: The scientific and appropriate utilisation of scarce productive resources to meet the unlimited wants of human beings like consumers, producers etc. is known as allocation of resources. - Define Production Possibility Curve.
Answer: Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is the graphical representation showing all the possible combinations of goods and services that an economy can produce with full employment of available resources within given time period. It is also called production possibility frontier. - Why is the production possibility curve called production possibility frontier also?
Answer: Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is also called production possibility curve because their concept are same. Both are the graphical representation of the maximum level of output than an economy can achieve by showing all the possible combinations of goods and services. - Define division of labor.
Answer: Division of labor is the separation of the work process into many parts, each part is assigned to an individual workers or a group of workers according to their ability, knowledge, training etc. - State the meaning of market economy.
Answer: An economy in which majority of the economic activities like production, consumption, exchange, distribution etc. are carried out by private sector for profit motive is called market economy. It is also called capitalist economy or open economy. - What is the meaning of mixed economy?
Answer: Mixed economy is an economy where the economic resources are owned and managed by both the private sectors and the government. It is an economic system which consists of the features of both market economy as well as command economy. - Clarify the meaning of socialist economic system.
Answer: An economy in which all the economic activities are carried out by the central government for public welfare is known as socialist economic system. It is also called command economy or planned economy.
Short Questions ( For 5 marks)
- Explain the concept of scarcity and choice.
Answer: Human wants are unlimited but the resources are limited. So, today’s economists have to deal with a wide range of economic problems like poverty, unemployment, inflation and shortage of high skilled labor, problems of global warming and many other problems. This is the fact that we have scarce resources to satisfy our unlimited wants. As a result of this problem, the next problem scarcity creates is to make a choice for all. So, scarcity and choice are the basic problems in economics.
A situation in which wants and needs are in excess of the available resources is called scarcity. The conceptual meaning of scarcity in economics is that the commodity becomes scarce because it command price or value. The term scarcity in economics means lack of enough resources to satisfy all desired wants of individuals, society and the nation as well. Economic resources are available in limited quantity and we can’t get all our needs and wants fulfilled. A commodity is scarce, in economic sense not because it is rare or unavailable in the market but because the means to purchase it are limited.
The act of fulfilling any wants or needs by economic agent out of many is called choice. All economic agents face the problem of choice due to unlimited wants and limited resources. Choice explains the concept that resources are scarce; so choices have to be made by consumers, producers, firms and governments. The optimization objective of economic actors needs making an appropriate choice in the use of available resources. Choice is involved in economic activities at both consumption and production levels. It is also related with individuals and the nation as well. - Explain the various problems of allocation of resources.
Answer: The scientific and appropriate utilization of scarce productive resources to meet the unlimited wants of the human beings is known as allocation of resources. There are various problems related to allocation of resources and some of them are explained below:
a) What To Produce: The first problem related with resource allocation is “what goods and services to produce; and by how much or what quantities ?” because of scarcity of productive resources, production of all goods and services needed by a society or a nation are beyond its capacity. So, a firm and a society must choose from among various alternatives. For example: whether to produce vehicle to improve living standard or to produce weapons to improve defense.
b) How to produce: The second problem related to allocation of resources is concerned with the methods of production. If more labors are used in the production, it is called labor-intense technology. On the other hand, when more capital are used in production process, it is called capital-intensive technology. Labor-intensive technology creates more jobs and helps to minimize unemployment. On the other hand, capital-intensive technology is suitable for large volume of production. It facilitates for rapid economic growth.
c) For whom to produce: Due to the scarcity of resources, we can’t satisfy all wants of all the population. So, decision have to be taken concerning how many of each person’s want are to be satisfied. In the other words, before production of goods and services, the targeted consumer group should be identified.
d) Balanced Sectoral Development: There should be regional balance. All sectors of the economy should be given equal priority when allocating resources. The development of primary, secondary and tertiary sectors should all be balanced. - Describe the concept of Production Possibility Curve (PPC) with the help of table and diagram.
Answer: Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is the graphical representation showing all the possible combinations of goods and services that an economy can produce with full employment of available resources within given time period.
Assumptions
1. The economy produces only two goods: TV sets & Computers
2. There is full employment in the economy.
3. There is no change in the state of technology.
4. There is perfect mobility of resources from one use to another.
5. Time period is given.
On the basis of these assumptions, the concept of PPC can be explained with the help of the following table and diagram.
| Combinations | TV Sets | Computers |
| A | 0 | 15 |
| B | 1 | 14 |
| C | 2 | 12 |
| D | 3 | 9 |
| E | 4 | 5 |
| F | 5 | 0 |
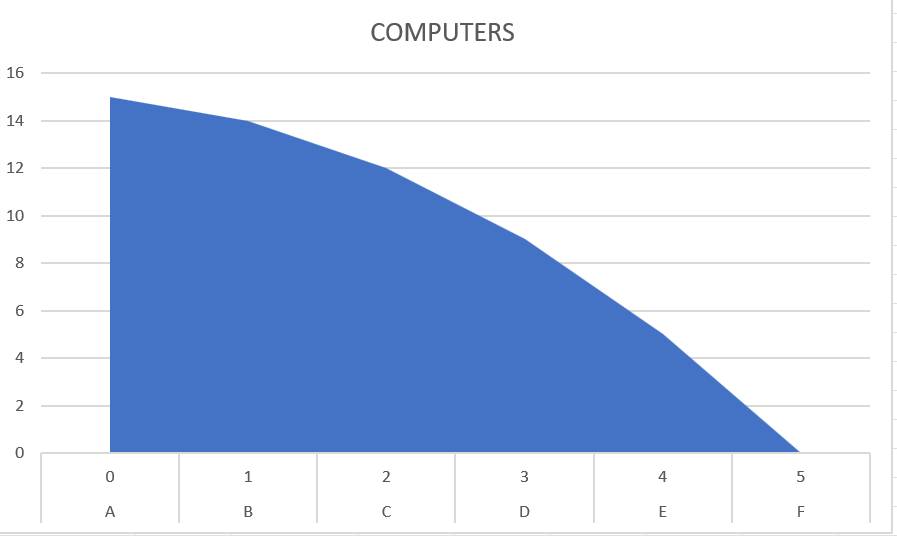
In the figure, units of TV sets and Computers are measured along the x-axis and y-axis respectively. A, B, C, D, E and F are the combinations of TV sets and computers. Joining these combinations, we get a line AF which is called PPC.
Any combination lying outside the PPC unattainable and any combination lying inside the PPC is inefficient. Only the combination lying on PPC are efficient. Hence, PPC is also called “Production Possibility Frontier”.
4. Explain in detail about the shift in production possibility curve.
Answer: Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is the locus of all combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce with the full and efficient utilization of all resources using the given technology and a given time period.
The movement of entire PPC from its initial position to inward and outward position, due to various reasons is called shift in PPC. The production possibilities of a nation change over time with the change in labor productivity, investment in productive sector, discovery of new sources of raw materials, size of active population and technology.
Causes Of Outward/Leftward Shift in PPC
1. Due to increase in labor productivity.
2. Due to increase in investment in productive sector.
3. Due to discovery of new sources of raw materials.
4. Due to increament in size of active population.
Causes of Inward/Rightward Shift in PPC
1. Due to backwardness in technology.
2. Due to decrease in labor productivity.
3. Due to decreament in investment in productive sectors.
4. Due to depletion in sources of raw materials.
5. Due to decrease in size of active population.
Hence, increase in the quality and quantity of resources shifts the PPC outwards as shown in the figure. Similarly, the decrease in quality and quantity of resources shifts the PPC inwards.


Definitely believe that which you said. Your favorite justification seemed to be at the web the easiest factor to have in mind of. I say to you, I definitely get irked even as other people think about worries that they plainly do not recognize about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top as neatly as defined out the whole thing with no need side effect , folks could take a signal. Will likely be again to get more. Thank you
I like this weblog very much, Its a rattling nice place to read and find information.
Great info and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is actually the best place to ask but do you guys have any thoughts on where to hire some professional writers? Thx 🙂
Very Nice ! Keep it up